本文共 15643 字,大约阅读时间需要 52 分钟。
一、前言
上一篇我们结束了 Bean 的注册与扫描,本篇我们将走进 Bean 的实例化和初始化。
二、源码分析
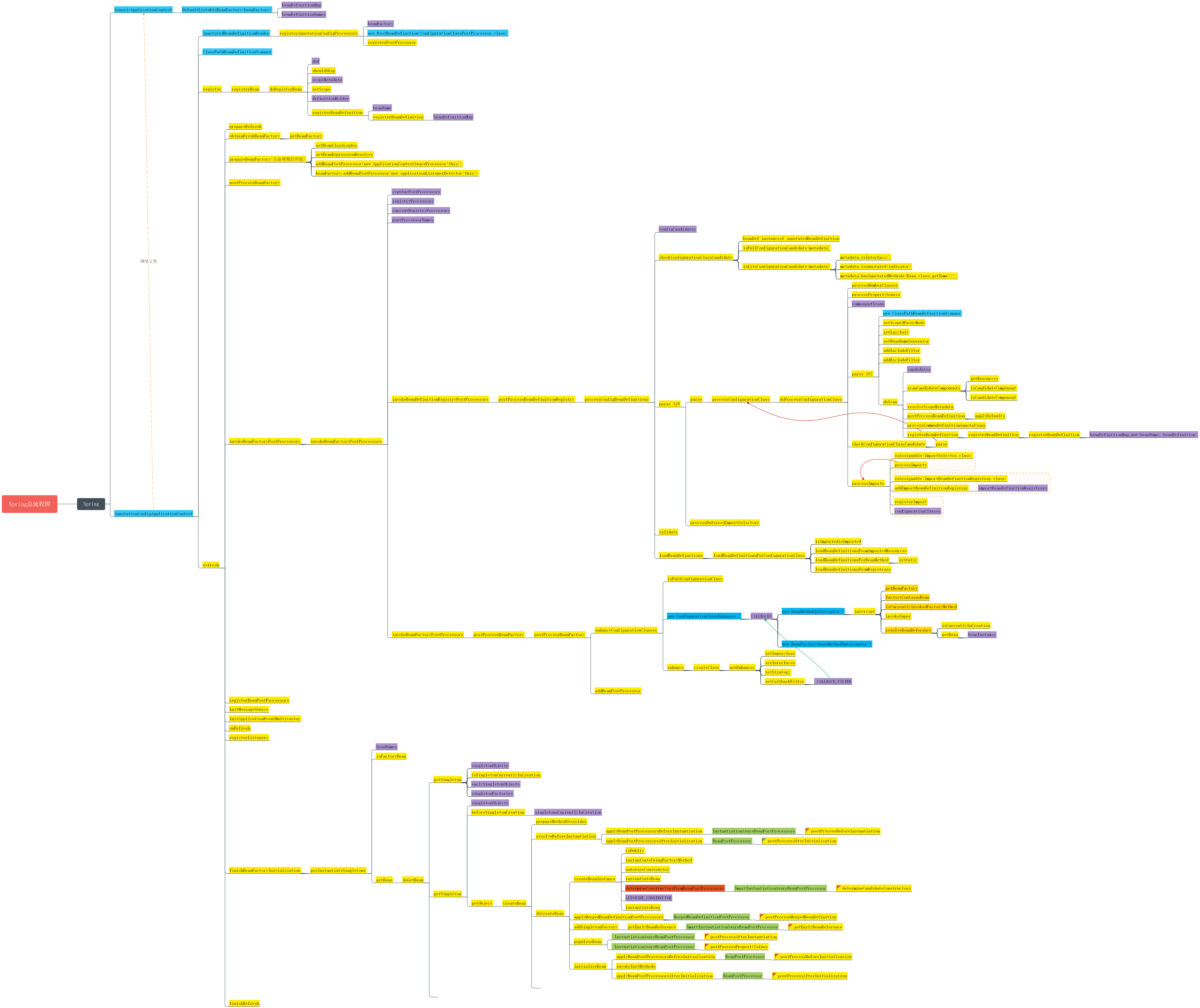
我们首先开一张思维导图,Bean 的实例化和初始化主要在 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); 这个方法里面完成。

我们可以随着思维导图一步一步跟进,调用 getBean,doGetBean,在 doGetBean 里面会两次调用 getSingleton,我们可以先看第一次调用。
这里会先判断一级缓存 singletonObject 是否为空,第一次调用一般都为空,然后判断 isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) 是否正在创建,主要是判断 singletonsCurrentlyInCreation 这个集合里面有没有Bean 的名字,我们可以发现前面并没有往这个集合里面添加,所以不会执行,直接 return 了。
@Nullableprotected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) { Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName); //判断是否正在创建 if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName); // if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) { ObjectFactory singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName); if (singletonFactory != null) { // singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject(); this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject); this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName); } } } } return singletonObject;} 如果第一个 getSingleton 可以拿到值,不为空,就不会执行第二个getSingleton。
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference"); } else { logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'"); } } //不等于空直接返回 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);} 第二次调用 getSingleton,这里将会去创造我们的 Bean,这里将会 9 次执行 5 个后置处理器。
//第 二 次调用 getSingleton,和第一个不是同一个getSingleton// Create bean instance.if (mbd.isSingleton()) { sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> { try { // return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. destroySingleton(beanName); throw ex; } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);} 1、第一次调用后置处理器 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors 的 postProcessBeforeInstantiation 方法,这个方法在目标对象被实例化之前调用,返回类型的 Object。这个时候对象还未被实例化,这个方法的返回值可以替代原来的对象,如果这个方法返回了一个值,那 Spring 接下来就只会执行 BeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法,并直接返回 Bean,下面的代码将不会执行,否则将继续按照流程继续走下去。
try { //第一次调用后置处理器 //bean实例化前后置处理器,如果后置处理返回的bean不为空,则直接返回 // Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance. Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse); //如果bean不为空直接返回 if (bean != null) { return bean; }} @Nullableprotected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { Object bean = null; //beforeInstantiationResolved有没有设置 if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) { // Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point. //判断是否设置过InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { Class targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd); if (targetType != null) { //applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName); if (bean != null) { bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName); } } } mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null); } return bean;} 2、如果上面一步返回的对象为空 ,将会执行下面的方法。
第二次调用后置处理器 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的 determineCandidateConstructors 方法,检测 Bean 的构造方法,并推断构造方法,以哪个构造方法实例化。
//创建beanObject beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { // Instantiate the bean. //Wrapper 包装,bean的包装 BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; if (mbd.isSingleton()) { instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); } if (instanceWrapper == null) { //第二次调用后置处理器 //实例化bean,把对象创建出来 instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); } protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) { // Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point. Class beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName); //检测一个类的创建权限,spring默认情况下对非public的类是允许访问的 if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName()); } Supplier instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier(); if (instanceSupplier != null) { return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName); } //如果工厂方法不为空,则通工厂方法构建bean对象 //1、通过FactoryMethod创建对象 if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) { return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args); } //多次构建一个bean时可以使用Shortcut(快捷方式) // Shortcut when re-creating the same bean... boolean resolved = false; boolean autowireNecessary = false; if (args == null) { synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) { if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) { resolved = true; //如果已经解析了构造方法的参数,则必须要通过一个带参构造方法来实例 autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved; } } } if (resolved) { if (autowireNecessary) { //2、通过构造方法自动装配的方式构造Bean return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null); } else { //3、通过默认的无参构造方法进行 return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd); } } //第二次执行后置处理器 //由后置处理器决定返回哪些构造方法 //自动装配的模型!=自动装配技术 //5 种模型,默认为 NO,直接忽略??? //AUTOWIRE_NO,AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME,AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE,AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR,AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT //模型是NO,采用的是ByTe自动装配的技术 // Candidate constructors for autowiring? Constructor [] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName); if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR || mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) { return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args); } // No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor. //返回空就会使用无参的构造方法 return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd); } @Nullableprotected Constructor [] determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(@Nullable Class beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException { // if (beanClass != null && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; //通过哪些构造方法实例化对象 Constructor [] ctors = ibp.determineCandidateConstructors(beanClass, beanName); if (ctors != null) { return ctors; } } } } return null;} 3、第三次调用后置处理器 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 的 postProcessMergedBeanDefinition 方法,找出并缓存对象的注解信息。
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) { if (!mbd.postProcessed) { try { //第三次调用后置处理器 //执行后置处理器 applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex); } mbd.postProcessed = true; }} protected void applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class beanType, String beanName) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor bdp = (MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) bp; bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName); } }} 4、第四次调用 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的 getEarlyBeanReference 方法,提前暴露对象。
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));if (earlySingletonExposure) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName + "' to allow for resolving potential circular references"); } //第四次调用后置处理器 //getEarlyBeanReference获取提前暴露的对象 //四个集合Map addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));} protected Object getEarlyBeanReference(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) { Object exposedObject = bean; if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; exposedObject = ibp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName); } } } return exposedObject;} protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory) { Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null"); synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { // if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) { this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory); // this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName); //所有被创建的对象 this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName); } }} 这里会判断一级缓存 singletonObjects 有没有对象,如果没有,就会放到三级缓存 singletonFactories 中去,这个三级缓存也是 Spring 解决循环依赖的核心。
//第五,六次调用后置处理器//赋值属性,完成自动装配populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
5、第五次调用后置处理器 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessAfterInstantiation 方法,这个方法在对象实例化之后调用,这个时候对象已经被实例化,但是该对象的属性还没有被设置,如果该方法返回 false额,将会忽视属性值的设置,如果返回true,将会按照正常流程设置属性
//需不需要spring来设置属性boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { //第五次执行后置处理器 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; //InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 实现这个接口,返回bean,spring会认为不需要设置属性 if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) { continueWithPropertyPopulation = false; break; } } }} 6、第六次调用后置处理器 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessPropertyValues 方法,对属性进行填充,完成自动注入,我们还可以修改原本该设置进去的属性,如果 postProcessAfterInstantiation 返回 false,该方法不会调用。
if (hasInstAwareBpps) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { //第六次执行后置处理器 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; //自动装配,完成注入 pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName); if (pvs == null) { return; } } }} //第七第八次,初始化exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction 7、第七次调用后置处理器 BeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法
@Overridepublic Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null) { return result; } result = current; } return result;} 8、第八次调用后置处理器 BeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法,
@Overridepublic Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; //第八次调用后置处理器 for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null) { return result; } result = current; } return result;} BeanPostProcessor 是 Spring 的一个扩展点,通过实现 BeanPostProcessor ,我们可以实现以下功能:
1、程序员可以插手 Bean 的实例化过程,从而减少 Bean 工厂的负担。
2、实在例化之后执行,也就是从 beanDefinition 里 new 出来一个Object 后,beanPostProcessor 插手之后,才会放到容器里面。 3、定义一个类实现了BeanPostProcessor,默认是会对整个Spring容器中所有的bean进行处理。 4、这个接口可以有多个类实现,形成一个列表,依次执行。最后再加上一张总的思维导图
三、结语
最后,我们再来总结一下
首先,在完成一个 Bean 的扫描与注册之后,我们就会开始一个 Bean 的实例化和初始化,实例化和初始化是两个不同的概念,实例化是简单的把一个 Bean 给 new 出来,还没有设置初始值,初始化是完完全全把一个可用的 Bean 给创造了出来。实例化和初始化的流程如下:
首先我们调用 getBean,doGetBean 之后,会调用两个 getSingleton 方法,然后再第二个 getSingleton 里面,我们将 8 次调用 5 个后置处理器,完成 Bean 的实例化和初始化。
1、调用 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors 的 postProcessBeforeInstantiation 方法,这个后置处理器继承了 BeanPostProcessor ,它内部提供了 3 个方法,加上 BeanPostProcessor 的 2 个方法,一共有 5 个方法。postProcessBeforeInstantiation 这个方法在目标对象实例化之前调用,该方法可以返回任何值,这个时候目标对象还没有实例化,所以这个返回值可以替代本应该返回的对象,如果这时候该方法返回了一个值,接下来只会调用 BeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法,其他步骤不再执行,否则,将会按照正常流程走。
2、调用 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的 determineCandidateConstructors 方法,该方法主要是推断构造方法,继而实例化 Bean,如果没有推断出来,将会使用默认构造方法完成 Bean 的实例化。
3、调用 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 的 postProcessMergedBeanDefinition 方法,找出所有需要注入的点(加了@Resource,@Autowired,@Value注解的属性),但此时还没有进行注入,注入是另外一个后置处理所做的事情。
4、调用 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的 getEarlyBeanReference 方法,提前暴露 Bean,主要用来解决循环引用的问题。
5、调用 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessAfterInstantiation 方法,在目标方法实例化之后调用,这时候对象已经被实例化,但属性还没有被设置,只要有一个后置处理器的该方法返回 false,都将会忽视属性的设置,如果返回 true,将会按照正常流程走,Spring 所有后置处理器都是返回的 true。
6、调用 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessPropertyValues 方法,对属性进行赋值和修改,如果 postProcessAfterInstantiation 返回的值为 false,该方法将不会执行。
7,8、调用 BeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法和 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法,在这两个方法之间还会执行声明周期的回调。
为了更加直观的展现源码的调用过程,我绘制了一张思维导图!
为了更加直观的展现源码的调用过程,我绘制了一张思维导图! 为了更加直观的展现源码的调用过程,我绘制了一张思维导图!ABOUT
公众号:【星尘Pro】
github:
推荐阅读
转载地址:http://hdfsi.baihongyu.com/